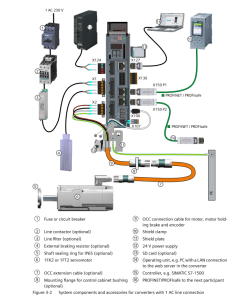
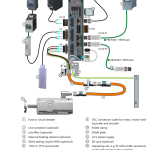
Handling HTTP Requests with Express.js – A Quick Guide
When building a Node.js app, Express makes it super easy to handle HTTP requests. Here’s a minimal example that shows how to:
- Send plain text, HTML, and JSON responses
- Handle different request methods (GET, POST, PATCH, DELETE)
- Return various HTTP status codes
- Use dynamic URL parameters
Let’s break it down.
📦 Setup
Start by requiring Express and setting up the app:
const express = require('express'); const app = express();
const port = 5555;app.use(express.json());
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: true }));🧭 Basic Routes
Root Route
Sends a simple “Hello World” message.
Logs the request.
app.get(‘/’, (req, res) => {
res.status(200).send(‘Hello World’);
});
Text, JSON, and HTML Responses
Plain Text:
app.get(‘/success’, (req, res) => {
res.status(200).send(‘Request successful!’);
});
JSON Response:
app.get(‘/successjson’, (req, res) => {
res.status(200).json([{ method: ‘GET’, message: ‘Request successful!’ }]);
});
HTML Content:
app.get(‘/successhtml’, (req, res) => {
res.status(200).type(‘html’).send(‘<h1>HTML World Response</h1>’);
});
⚠️ res.html() is not valid in Express. Use .type(‘html’).send() instead.
⚠️ Error Responses
Respond with standard HTTP error codes:
403 Forbidden
res.sendStatus(403);
404 Not Found
res.status(404).send(‘Resource not found.’);
500 Internal Server Error
res.status(500).send(‘An unexpected error occurred on the server.’);
🔄 Dynamic Routes with Params
Handle dynamic data using URL parameters:
app.get(‘/get/:id’, (req, res) => {
const { id } = req.params;
if (id === ‘1’) {
res.status(200).type(‘html’).send(`<h2>The id (${id}) is for Engineering Field</h2>`);
} else {
res.status(200).send(`Received GET request with Id: ${id}`);
}
});
✍️ Other HTTP Methods
POST:
app.post(‘/me/:id’, (req, res) => {
res.send(`Received POST request with Id: ${req.params.id}`);
});
PATCH:
app.patch(‘/pat/:id’, (req, res) => {
res.send(`Received PATCH request with Id: ${req.params.id}`);
});
DELETE:
app.delete(‘/del/:id’, (req, res) => {
res.send(`Request to delete id: ${req.params.id} completed`);
});
🚀 Start the Server
Finally, launch the server:
app.listen(port, ‘localhost’, () => {
console.log(`Server is listening on http://localhost:${port}`);
});
✅ Summary
With just a few lines, Express can:
- Respond with various content types
- Handle all major HTTP methods
- Deal with both static and dynamic routes
- Return correct status codes for success and errors
Whether you’re building APIs or testing simple routes, this setup gives you a solid starting point.