Branch Circuit Protection
Definition:
Branch protection refers to overcurrent protection for the final circuit segment that delivers power to individual loads or devices. This is the primary protection required by the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States for circuits that extend from a panelboard to an end-use device.
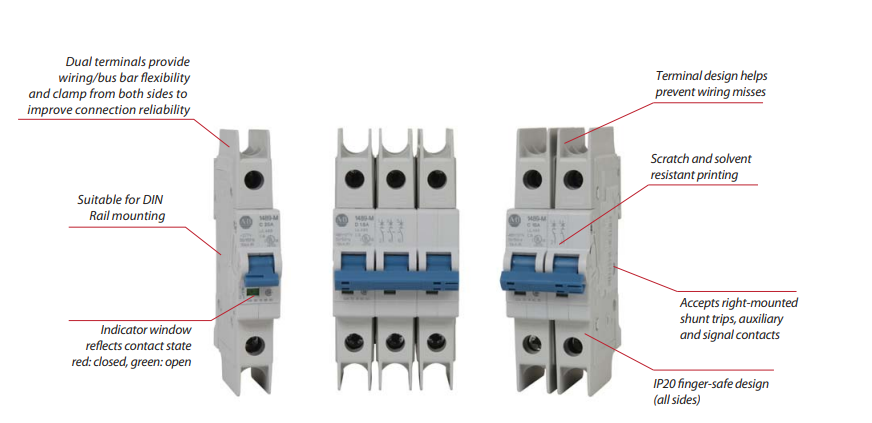
Key Features:
-
Must comply with UL 489 standard.
-
Required by code for safety and legal compliance.
-
Protects against short circuits and overloads.
-
Typically installed at the panel level (e.g., in panelboards or distribution boards).
-
Has a high interrupting capacity to safely disconnect in the event of a fault.
Applications:
-
Protecting lighting circuits, outlets, motors, and industrial machinery.
-
Used in residential, commercial, and industrial power distribution systems.
Supplementary Protection
Definition:
Supplementary protection is additional overcurrent protection for specific components or equipment within a system that is already protected by branch circuit protection. These devices are not intended to protect branch circuits and are not recognized as a substitute for UL 489 devices.
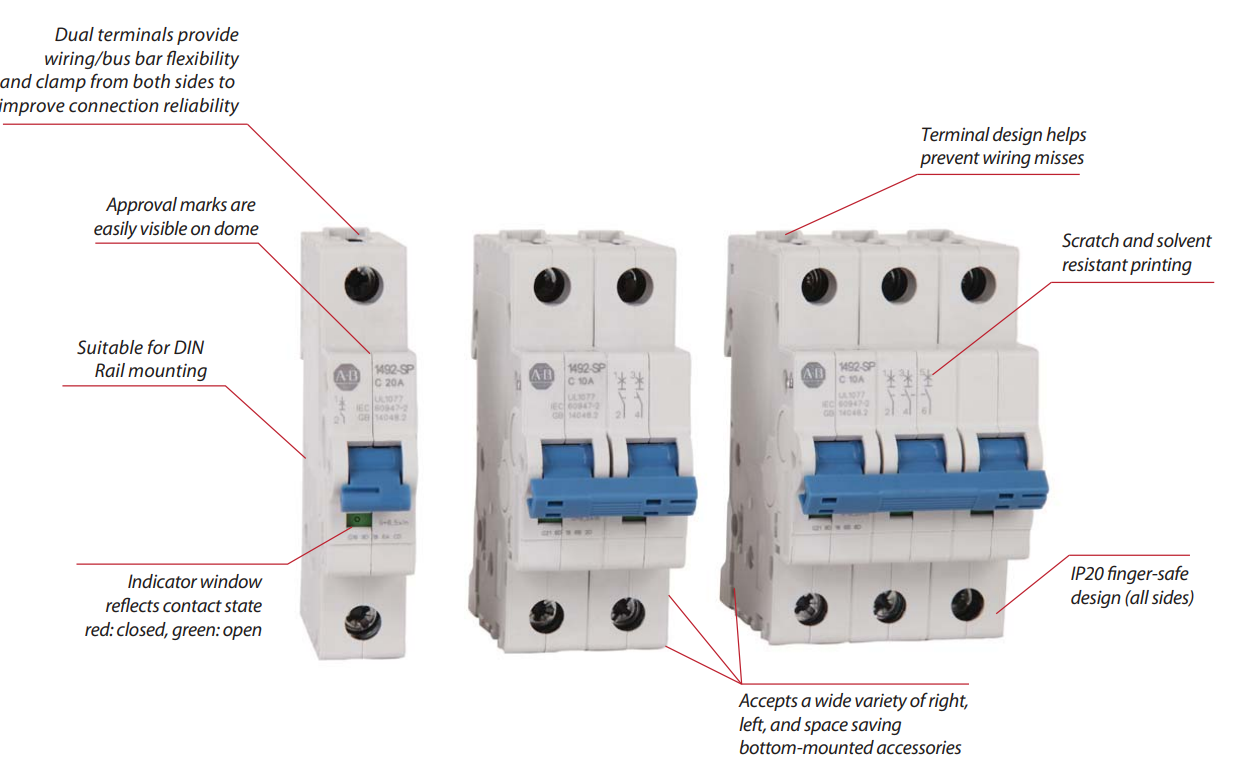
Key Features:
-
Complies with UL 1077 standard.
-
Provides localized protection for internal components, such as control circuits or electronic boards.
-
Typically has lower interrupting capacity.
-
Compact, cost-effective, and suitable for OEM equipment or control panels.
-
Often mounted on DIN rails inside enclosures.
Applications:
-
Protecting PLC I/O modules, sensors, small power supplies, or control transformers.
-
Used where multiple internal components need individual protection downstream of a UL 489 breaker.
| Feature | Branch Protection (UL 489) | Supplementary Protection (UL 1077) |
| Purpose | Primary circuit protection | Additional/internal device protection |
| Code Requirement | Yes (NEC compliant) | No (optional, not code-required) |
| Interrupting Capacity | High | Moderate to low |
| Installation Location | Panelboards, distribution circuits | Inside equipment or control panels |
| Typical Use | Power circuits, final load protection | Protection of internal or control devices |
Image credit: Rockwell Automation
#overcurrent #short #circuits #overloads.