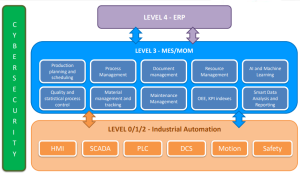
The digital transformation of the manufacturing industry is reshaping the landscape, driven by technological advancements and the need for greater efficiency, quality, and sustainability. At the heart of this transformation is the Manufacturing Execution System (MES)—a critical technology that bridges the gap between Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and the shop floor. Implementing MES is a complex project that introduces significant changes, particularly in production environments. To maximize its benefits, it’s essential to properly define the scope of MES-driven changes. One of the most reliable frameworks for MES design and implementation is the ISA-95 standard.
ISA-95 and MES Design Phases
The ISA-95 standard divides the MES design into two key stages:
-
Basic Design Stage
The basic design focuses on documenting the system’s overall structure using descriptions and flow chart diagrams. This stage provides a high-level overview of MES functionality and workflows.
-
Detailed Design Stage
This phase involves drafting comprehensive MES system and interface requirements using Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagrams. Detailed design defines how different components interact and ensures the system is ready for seamless integration and implementation.
Key Goals of MES Implementation
Implementing MES helps manufacturers achieve several critical goals:
-
Supply Chain Optimization: Enhanced workflow control and real-time process documentation improve the entire supply chain’s efficiency.
-
Improved Data Quality: Accurate data allows better process and product evaluations.
-
Enhanced Production Visibility: Only process deviations require analysis, reducing the need for constant manual checks.
-
Lower Work-In-Progress (WIP) Costs: Reduced lead times lower storage costs for WIP materials.
-
Reduced Administrative Work: Automating the maintenance of manufacturing documents minimizes manual administrative tasks.
-
Fewer Lost Batches: MES implementation decreases the risk of lost or incomplete production batches.
-
Reduced Operating Costs: Integration of MES prevents isolated systems, lowering overall costs.
-
Better Decision-Making: Easy access to current data improves decisions across all critical business cases.
The ISA-95 framework helps minimize risks during MES implementation, ensuring manufacturers achieve these benefits.
Benefits of MES Implementation Recent research highlights the substantial benefits MES offers for manufacturers undergoing digital transformation:
-
Operational Efficiency
MES streamlines production processes with real-time monitoring and control. Companies often see reduced downtime and better resource utilization, improving overall production efficiency.
-
Product Quality
MES enhances traceability and quality control throughout production, leading to fewer defects and increased compliance with quality standards.
-
Real-Time Decision-Making
By providing real-time data and analytics, MES empowers managers to make quick, informed decisions to address production issues, optimize workflows, and enhance plant performance.
-
System Integration
MES integrates with cutting-edge technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), Big Data analytics, and cloud computing. This integration facilitates data sharing and advanced analytics, driving process optimization and continuous improvement.
Challenges in Implementing MES Systems
Implementing Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) can significantly enhance operational efficiency, product quality, and decision-making. However, the process is not without its challenges:
Integration with Legacy Systems
MES must often integrate with existing ERP and shop floor systems. Ensuring compatibility and seamless data exchange can be complex.
High Implementation Costs
The initial cost of MES software, hardware, training, and customization can be a significant barrier, especially for smaller manufacturers.
Change Management
MES implementation involves process changes that may face resistance from employees. Proper training and clear communication are crucial for adoption.
Data Accuracy and Standardization
MES relies on accurate data inputs. Inconsistent or inaccurate data can lead to poor decision-making and diminished system effectiveness.
Customization and Scalability
Manufacturers often need customized MES solutions that fit their unique production needs. Ensuring future scalability can add complexity to the implementation.
Security Concerns
As MES becomes more interconnected with IoT and cloud systems, cybersecurity risks increase. Robust security protocols are essential to protect sensitive production data.
Downtime During Transition Implementing MES can lead to temporary production downtime. Proper planning and phased rollouts are necessary to minimize disruptions. Addressing these challenges with strategic planning, effective change management, and robust training programs can help manufacturers successfully implement MES and maximize its benefits.
Conclusion
The ISA-95 standard is essential for designing and implementing a robust MES system. By adopting best practices for MES integration, manufacturers can achieve improved operational efficiency, enhanced product quality, real-time decision-making, and seamless system integration. As the industry evolves, embracing MES and future technologies will be key to staying competitive in the digital era.
References:
Govindaraju, Rajesri, and Krisna Putra. “A methodology for Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) implementation.” IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. Vol. 114. No. 1. IOP Publishing, 2016.
image credit:prismagroup