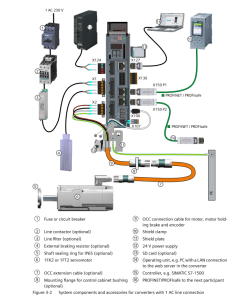
Overview of Functional Safety
Functional safety refers to the set of measures implemented through electrical, electronic, and programmable systems to prevent or eliminate hazards caused by functional errors. Its main objective is to ensure that machinery operates safely even when faults occur. During normal operation, protective devices prevent human access to hazardous areas. However, in certain modes—such as maintenance or setup—operators may need to be within danger zones. In such cases, internal drive and control safety measures protect the operator from harm.
Integrated Functional Safety
Integrated functional safety provides built-in protective functionalities within control systems and drives. This approach simplifies planning and installation, reducing both cost and complexity. By incorporating safety features directly into the system architecture, machine functionality and uptime are improved. Integrated safety ensures compliance with the Machinery Directive, offering reliable protection for personnel working on or near machines.
Safety Components and Their Role
The inverter’s safety component provides the necessary safe interfaces, such as safe inputs and safe communication over safety networks. When a Safe Torque Off (STO) function is triggered, the safety component immediately switches the drive to a torque-free state, as specified in EN 61800-5-2. Safety components are typically identified with yellow markings to distinguish them from standard components.
Standards and Compliance
Functional safety requirements are governed by international standards, laws, and technical regulations. Compliance ensures that equipment and systems meet recognized safety expectations. Depending on the specific application, relevant regulations must be carefully reviewed and implemented.
The Importance of Risk Assessment
Before a machine can be marketed or operated, a risk assessment must be conducted in accordance with the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC (or UK equivalent S.I. 2008/1597). This assessment identifies potential hazards and determines the required safety measures.
The directive emphasizes three core principles:
-
Eliminate or minimize hazards through design.
-
Implement protective measures against unavoidable hazards.
-
Document residual risks and inform users accordingly.
Detailed guidelines for performing a risk assessment are provided in DIN EN ISO 12100:2013-08 – Safety of Machinery: General Principles for Design, Risk Assessment, and Risk Reduction. The outcome of the assessment determines the safety category and performance level of control systems as defined in EN ISO 13849-1.
Summary
Functional safety is an essential aspect of modern machine design, ensuring operator protection through intelligent control, integrated safety components, and adherence to international standards. By combining risk assessment, design optimization, and compliance with safety directives, manufacturers can achieve high machine availability while maintaining the highest level of human safety.
#PLC #capacityautomation #Scadasystem #amazing design #
ImageCredit: Autodesk